Unit 9 Reflection
Unit 9
Hello Readers it is finally the end of another unit and as always I am here to give you a summary on what I learned and what I take away from this unit. Unit 9 was very classification based and is a huge run down of most, if not all of the different organisms in our world, from elephants to bacteria. In fact that brings us to our first topic of bacteria. I learned that they come in 3 basic shapes: Spheres, Rods, and Spirals. The cell walls are made of peptidoglycan and that most move with flagellum.
As shown above.
Chemoheterotrophs: Eat other Bacteria
Photoautotrophs: Use light to convert carbon and water into compounds
Chemoautotrophs: Get energy from chemical reactions
Aerobes, need oxygen to survive, unlike Anarobes which oxygen kills them. The very adaptive ones are Anaerobes which can need a mixture of both to survive.
Some uses of bacteria are:
- Decomposition
- Fermentation
- Medicine
- Biofuels
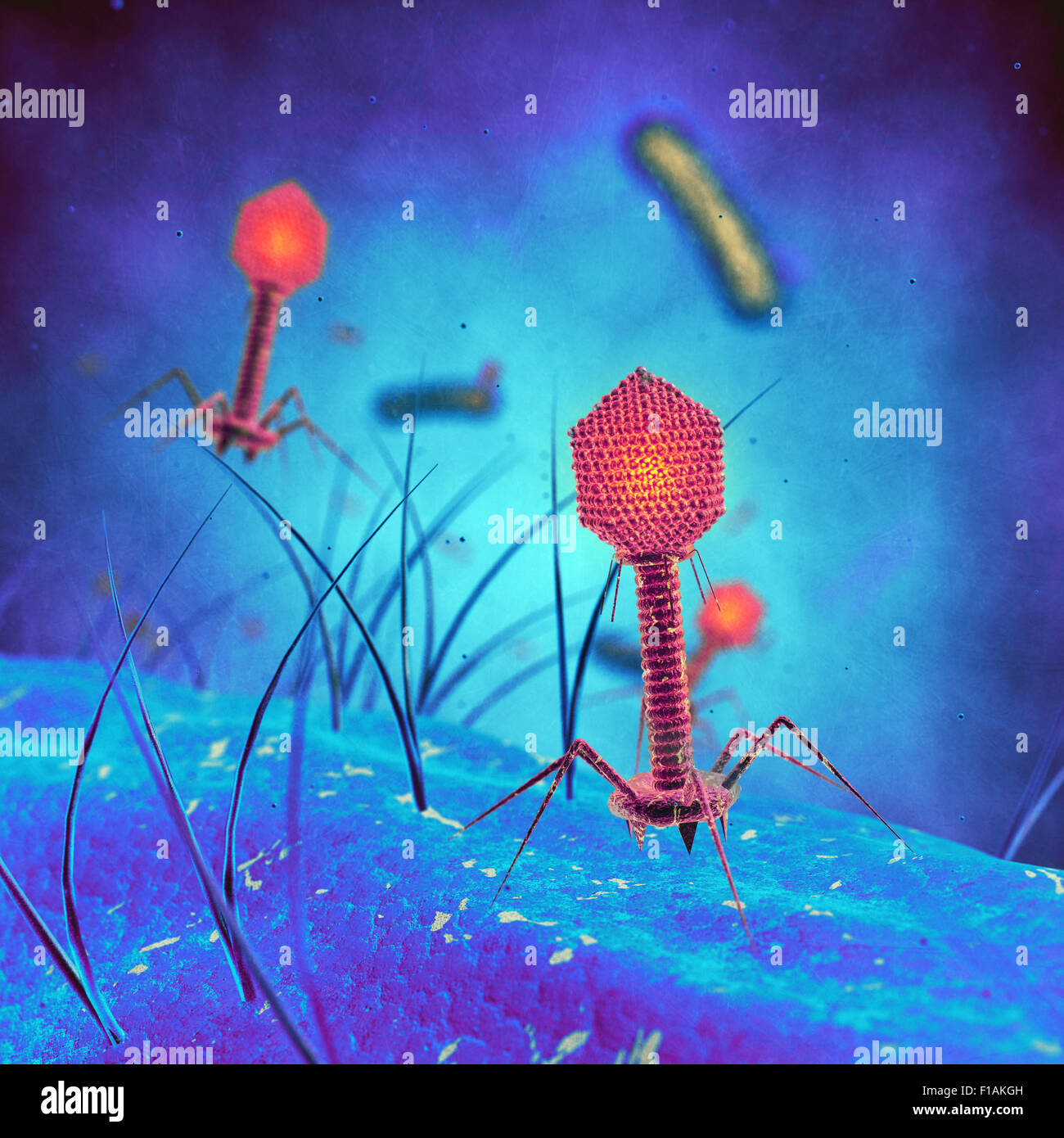
They usually multiply by taking over a cell and using it's resources to make more copies of itself, eventually killing the host cell. A well recognized Virus is the Bacteriaphage which injects its' DNA in cells to multiply ans kill the cell.The reason we get sick from Viruses make us sick is because they kill our cells or they produce toxins.
 Our next stop is Fungi. Fungi is most commonly know as mushrooms but there are others such as Bread Molds. They have cell walls made of chitin and absorb their food through nyphae. Fungi use spores to reproduce and disperse, and have many uses.
Our next stop is Fungi. Fungi is most commonly know as mushrooms but there are others such as Bread Molds. They have cell walls made of chitin and absorb their food through nyphae. Fungi use spores to reproduce and disperse, and have many uses.- Food
- Antibiotics
- Hallucinations
Now we get to plants, and they are a good indicator of evolution because they are so diverse. If you want more on genetics or diversity click on this Link. One major adaptation to get away from the riverbanks was the cuticle. It is a waxy protective layer that stopped plants from drying out, and an extreme example of this are those very waxy cacti. They also got more adept at vascular systems to allow resources to get through the plant. A huge advantage was pollen because it allowed reproduction without free standing water.
The major plant Phyla are:
- Mosses (Bryophyta)
- Ferns (Pterophyta)
- Cone plants (Gymnosperms)
Some of the others include Cyrads (Palm Tree like), Ginkgos (last one left), Conifers (most common).
- Angiosperms
Monocots: leaf veins parallel, and have flowering parts usually in 3's, Vascular tissue in stem
Dicots: Leaf veins net like, Flowering parts in 4's or 5's, Vascular tissue in rings of stems
- Sponges and Cnidarians
- Polyps (anemones)
- Medusa (jellyfish)
- Scyphozoans (Jellyfish)
- Anthozoans (Coral, Anemones)
- Hydrozoans (Hydra)
- Cucozoans (Boxjelly)
- Flatworms
- Planarians
- Flukes
- Tapeworms
- Molluska
3 classes are:
- Gastropods (snails and slugs)
- Bivalyes (Clams, Oysters and Mussels)
- Cephalopods (Octopus, Squid and Cuttlefish)
- Earthworms
- Marine Worms
- Leeches
- Trilobites
- Crustaceans
It includes:
- Decapods
- Barnicles
- Isapods
- Chelicerates
- Insects
- Myriapods
- Echinoderms
The last group we identified was Chordates. All of them have some common traits (like a backbone) and an endo-skeleton allows them to grow bigger than invertebrates. They all have 4 features while developing; notochord, hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, tail.
- Agnath
- Hagfish
- Lampreys
- Condrictheyes
2 classes are:
- Condrictheyes (Sharks)
- Osteictheyes (Regular Fish)
- Osterictheyes
- Amphibia
2.Salamanders
long body, 4 limbs and tail, 300+ species
2.Frogs and Toads
3000+ species, can be poisonous
3.Caecilians
legless, burrowing, 160+ species
All of these listed are amniotes, 2 circuit blood vessels.
3 Chambered heart: Reptiles and Amphibians
4 Chambered heart: Birds and Mammals
Ecto: Cold blooded
Endo: Internally warm blood
- Reptiles
- Turtles, Tortoises, and Terrapins
- Snakes and Lizards
- Crocodillians
- Birds (Avians)
- Mammals
Thanks for reading!!!
Here is more on a project I did
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/12mQx-N86bFId2EL_Suw99pZHYAuVE7ixedxe-HYaP2U/edit?usp=sharing
https://impremedia.net/bacterial-flagellar-motor-animation/
https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bacteriophage-viruses-infecting-bacterial-cells-86901377.html
https://sciencing.com/fungus-vs-mold-5529716.html

Comments
Post a Comment